
Understanding the nuances of making adjusting entries in different accounting systems requires specialized knowledge and training. This highlights the importance of continuous learning and professional development for accountants and financial professionals. Prepaid expenses require adjustments to reflect the expense in the period it pertains to, rather than when it was paid. While adjusting entries are commonly made at the end of an accounting period, they can also be made in the middle of a period if needed.

Interim Periods
As a small business owner, you probably find yourself juggling multiple roles, just like John, who runs a busy retail store in Austin. Between managing inventory, assisting customers, and ensuring his team is motivated, John barely has time to breathe. Adjusting entries for estimates are made to account for items that are typically not known with certainty until a later date, such as depreciation, amortization, and bad debt expense. HighRadius leverages advanced AI to detect financial anomalies with over 95% accuracy across $10.3T in annual transactions. With 7 AI patents, 20+ use cases, FreedaGPT, and LiveCube, it simplifies complex analysis through intuitive prompts. Backed by 2,700+ successful finance transformations and a robust partner ecosystem, HighRadius delivers rapid ROI and seamless ERP and R2R integration—powering the future of intelligent finance.

What is an example of an adjusting entry?
For example, if an adjustment entry is made to increase revenue, this will increase the business’s profitability for that period. Conversely, if an adjustment entry is made to increase expenses, this will decrease the business’s profitability for that period. Prepaid insurance is insurance that has been paid for but not yet used. To record prepaid insurance, an adjusting entry is made to decrease the asset account and increase the corresponding expense account. The revenue recognition principle requires businesses to recognize revenue when it is earned, regardless of when payment is received.
- Adjusting entries plays a vital role in the accounting cycle, which is the process of recording and processing all financial transactions within a specific accounting period.
- Maintain thorough documentation for all adjusting entries, including the reason for the adjustment, supporting calculations, and any relevant references to accounting standards.
- This transaction is recorded as a prepayment until the expenses are incurred.
- To record a prepaid expense, an accountant would debit an asset account and credit a liability account.
- Adjusting entries provides a mechanism to correct these errors without altering the original entries.
- It is usually not possible to create financial statements that are fully in compliance with accounting standards without the use of adjusting entries.
Adjusting Entry for Unearned Income
- To better understand how adjusting entries work, let’s go through a practical example.
- An adjusting journal entry is made to record this incremental, non-cash transaction for each accounting period within the lifespan, at the end of which the value of the asset will have reached zero.
- The point is to make your accounting ledger as accurate as possible without doing any illegal tampering with the numbers.
- Reviewing several examples helps accountants catch timing errors, compare patterns across periods, and verify whether accrued items or deferrals have been properly updated.
- The $25,000 balance in Equipment is accurate, so no entry is needed in this account.
The software can automate parts of the process and generate financial statements for you. However, you’re still responsible for ensuring that adjusting entries are accurate and completed on time. The software simplifies the task but doesn’t eliminate the need for careful oversight and accuracy. This includes not just the obvious outlays, but also accrued expenses such as payroll and services received but not yet billed. For example, if a adjusting entries examples computer repair needed at the end of February is not invoiced until March, the expense should still be recorded in February to reflect the true costs incurred during that month. Common examples include accruals of revenues or expenses that have been earned or incurred but not yet recorded, and adjustments for prepaid expenses, such as insurance, that should be apportioned over time.
Cash Flow
A word used by accountants to communicate that an expense has occurred and needs to be recognized on the income statement even though no payment was made. The second part of the necessary entry will be a credit to a liability account. The $25,000 balance in Equipment is accurate, so no entry is needed in this account. As an asset account, the debit balance of $25,000 will carry over to the next https://bluebeauty.mmindsdemo.com/columbus-ohio-cpa-firm-accounting-tax-and-business/ accounting year. The $1,500 balance in the asset account Prepaid Insurance is the preliminary balance. The correct amount is the amount that has been paid by the company for insurance coverage that will expire after the balance sheet date.

Thus, your bill for July is $4,000, but since you won’t be billing your clients until August 1, you’ll have to adjust the entry to amass the $4,000 you earned in July.
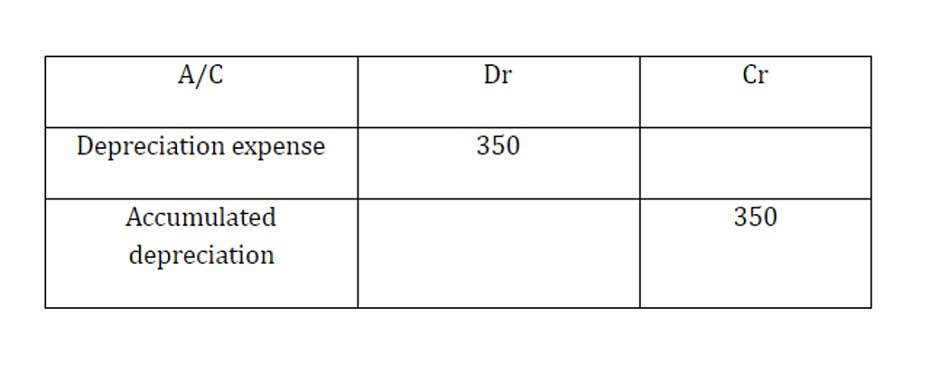
For example, if an adjustment entry is made to adjust the balance of a particular account that is related to a specific fiscal year, this will impact the financial statements for that fiscal year. Amortization is the allocation of the cost of an intangible asset over its useful life. To record amortization, an accountant would debit an expense account and credit an accumulated amortization account. For example, if a company has received payment for services that it has not yet provided, an adjustment entry is needed to record the revenue earned but not yet received.
- To illustrate how depreciation expense is computed, let’s use the straight-line method in our example for easier understanding.
- Under this arrangement December’s interest expense will be paid in December, January’s interest expense will be paid in January, etc.
- In accrual accounting, it’s imperative to record revenues and expenses when they are earned or incurred, irrespective of when cash is exchanged.
- For example, if an adjustment entry is made to defer revenue to a future accounting period, this will delay the recognition of revenue until the future period.
- The contra asset account which accumulates the amount of Depreciation Expense taken on Equipment since the equipment was acquired.
- To do so, you’ll have to use an adjusting journal entry, debiting Accounts Receivable and crediting Accrued Revenue.
Because Bad Debts Expense is an income statement account, its balance will not carry forward to the next year. Bad Debts Expense will start the next accounting year with a zero balance. To determine if the balance in this account is accurate the accountant might review the detailed listing of customers who have not paid their invoices for goods or services.
Balance Sheet
Adjusting entries are necessary to ensure that your financial statements reflect the actual financial position of your business at the end of an accounting period. Without these data entries, your income, expenses, assets, and liabilities may be misstated, leading to inaccurate financial reporting. An accrued revenue is the revenue that has been earned (goods or services have been delivered), while the cash has neither been received nor recorded. The revenue is recognized through an accrued revenue how is sales tax calculated account and a receivable account.
Leave a Reply